Which Feature(S) Of The Skin Protect(S) Us Against Microbes Such As Bacteria?
DISEASE CAUSING MICRO-ORGANISMS FACT Canvass
What are Disease Causing Micro-organisms?
How many times accept nosotros been told to wash our hands before sitting downwards at the supper tabular array or after touching money and other muddy surfaces? By washing up we call back that we're make clean and microorganism-free. Nosotros have baths, cook our food, treat our sewage and even cover our mouths when we coughing and sneeze to prevent the spread of those tiny dirty particles that could make us sick. What many people don't realize is that fifty-fifty after doing all of these things, we are nonetheless far from being make clean. The number of microorganisms living on and in us is about ten times higher than the number of cells that make up our entire body! Earlier you endeavour and scrub abroad those tiny organisms all over your pare, consider that most of these microorganisms are essential to our health.

Affliction-causing microorganisms, nevertheless, are another matter entirely. They use unproblematic tricks to enter our bodies and so they tin cause affliction. These germs have been studying ways to trick the human being immune system for a long time considering getting by the body's defences is key for their survival. Nosotros may even learn a matter or ii near the immune system past studying them. Who knew nosotros could learn from something so modest?
(All bolded terms are found in Glossary at end of this sheet).
What is a Microbe?

A microbe – another word for a microorganism – is a tiny individual living thing that is way too small to be seen by the human heart alone. The just way this tiny organism can be seen is past using a microscope. This is why microbes are often called "microscopic organisms." These organisms are found almost everywhere you can recollect of hither on Earth – in air, water, soil and stone, and even in plants, animals and the human body. Some microbes can alive in very hot temperatures, and others can live in the freezing common cold. Some demand oxygen to grow and stay alive, like you or I, while others survive without information technology. Below is a list of some good microbes that are found in our bodies.
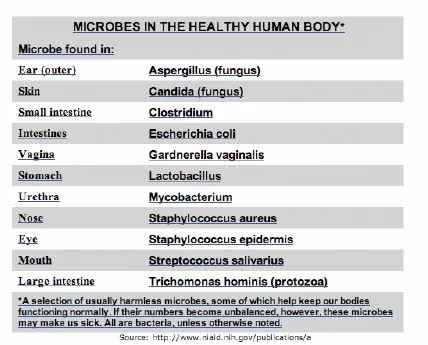
While some microbes play an important part in our daily lives by keeping united states salubrious, others are nil but bad news. These "bad-news" microbes are chosen affliction-causing microbes and can make humans, animals and plants sick by causing infection and affliction. About microbes vest to four major groups: leaner, viruses, protozoa or fungi. (To discover out more than, see the "Bacteria/Viruses/Protozoa" fact sheets). Disease-causing microbes can likewise exist called pathogens, germs or bugs and are responsible for causing infectious diseases. They tin can also contribute to chronic diseases and conditions, and are now being linked with coronary artery disease, diabetes, and sure types of cancer, multiple sclerosis and chronic lung affliction.

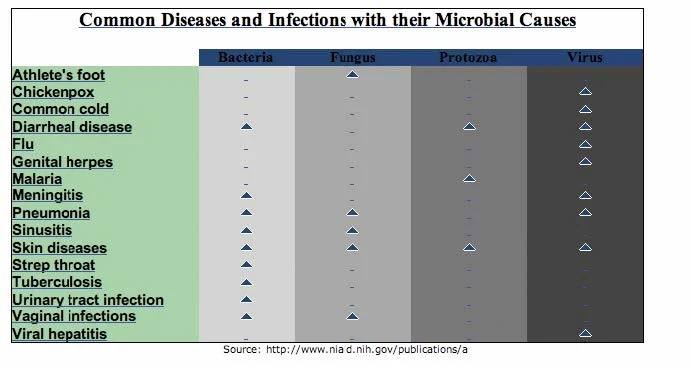
Microbes – the Ones that Make U.s.a. Sick
Infectious diseases caused by illness-causing microbes are responsible for more deaths worldwide than any other unmarried cause! Scientists are working hard to find ways that volition control these germs but trying to defeat them is non an piece of cake task. Illness-causing microbes are very adept at adjusting to new environments making it hard to find a mode to go rid of them. Microbes can speedily develop new features that make them resistant to the drugs that were once able to kill them. This means scientists must endeavour and stay i-step ahead, fifty-fifty though it is hard to do. New diseases caused past recently discovered pathogens are likewise being identified at an increasing rate. In the by thirty years about 30 new pathogens take been identified!
How Microbes Infect Us – The Nuts
How practise nosotros really become infected with a illness-causing microorganism? Here's the scoop!
Everyday we come into contact with people or animals that may be infected with affliction-causing microbes. This puts u.s.a. at risk of being exposed to illness.
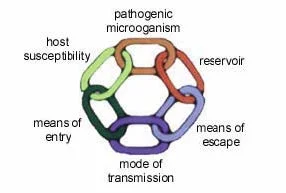
Becoming infected depends on the link betwixt the pathogen, the surround and the host - the host being you lot or I. The infection method may be idea of equally vi different steps that all join together to form a circular chain.

1. The procedure begins with a certain illness-causing microbe existence present. It is the first link in the concatenation.

2. The second link is the reservoir, the environment where the pathogen tin can survive. Examples of a reservoir include water, soil and within someone who is already infected with the germ.

iii. Having a mode to escape from the reservoir makes upwardly the 3rd link. If nosotros are the reservoir, the pathogenic microorganism can escape when we cough or sneeze.

4. The quaternary link of the concatenation is
the mode of manual from the reservoir to the host. If water is the reservoir, its style of transmission could be our drinking water supply.

5. To cause infection, the pathogen must find a way inside the host. Finding a means of entry is the fifth link. A pathogen in h2o would enter us if we drank the water it was in. A pathogen in the air would enter us if we inhaled information technology.

vi. The final link of the concatenation is how susceptible the host is to infection. Depending on the germ and the disease information technology causes, some hosts will be easier to infect than others.
For infection to occur each step has to be completed. If even one link of the concatenation is broken, the process will be interrupted and no infection volition occur. For example, the chain could be broken at link four, mode of transmission, or link six, host susceptibility. Both are shown here.

How Microbes Infect Us – The Specifics
Every type of germ has its own way of sneaking inside you to brand yous sick. By figuring out how germs infect u.s. we have a improve take a chance of avoiding infection in the futurity. Germs tin can be spread in many different ways. They can travel through the air, pass directly from person to person, are nowadays on surfaces contaminated by someone who is infected and exist spread past someone who may not even know they're sick. To find out more near the means these bad bugs cause infection, continue reading!
Just how can microbes travel through the air? It'southward not equally difficult as y'all may recollect. When someone coughs or sneezes without covering his/her mouth germs can spread everywhere! If you have a cold and cough without covering your oral cavity, your germs will travel through the air to where someone else may breathe them in. This gives the germs access to some other host it tin can infect and is the most common fashion to get infected with cold and flu viruses or the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. When we call back nearly how many times nosotros see people coughing or sneeze without covering their mouth, it's piece of cake to understand why and then many people get sick during the cold and influenza flavour, or why tuberculosis is known for existence so contagious.
As well traveling through the air, there is another mode germs are passed from person to person and it involves close, personal contact. How does this type of manual work? Well, we have more than than 500 types of microbes living in our mouths at this very moment. That's a lot of microbes! Some of these microbes are adept, while others are – you guessed information technology – the disease-causing kind. 1 style these microbes get passed from one person to another is by kissing. Another manner is by straight contact through sexual intercourse.
Touching objects or surfaces that accept been dirtied with germs is a way of being indirectly exposed to affliction-causing microbes. This commonly occurs by accidentally passing feces from your easily to your mouth or the mouths of others. Sound confusing? Let'due south expect at an example. Let's say someone is sick with a type of leaner that causes diarrhea. They use the bathroom often just don't take the fourth dimension to properly launder their hands each time. Their hands are at present contaminated with the leaner and when they touch some other surface, like a telephone or the Idiot box remote control, it becomes contaminated too. When someone else comes forth and uses either of these things, the leaner will transfer to their easily making them contaminated. If the newly contaminated hands are not washed earlier the person touches their oral fissure, the leaner will have a manner inside that person and be able to cause infection. This is what nosotros call fecal-oral manual. An important fact to recall is that indirect transmission may besides occur in a more direct way. Something equally uncomplicated as shaking hands with someone who coughed or sneezed on the same manus you're shaking will pass the germs. Indirect spread is not express to diarrheal illnesses – it is possible to laissez passer unlike types of germs this way. This blazon of transmission is common in daycare centres considering there are many children who are in contact with each other and with objects that may be contaminated, and nosotros all know how much young children like putting things in their mouths!

Unlike Germs and the Infections they Cause
When information technology comes to germs, there is nothing predictable almost them. Not merely practice they infect you lot in different ways, they can likewise crusade dissimilar sorts of infections. These infections are divided into three different groups based on the length of time they make you ill. Each infection type is explained beneath.
Acute infections last for a brusk amount of time and tin can be severe. These infections cause symptoms such as tiredness, muscle aches, coughing and sneezing. An example of an acute infection is the mutual cold. Acute infections concluding near two to twenty-four days with the boilerplate infection fourth dimension being well-nigh one week.
Chronic infections last anywhere from days to months to a lifetime and usually develop from astute infections. Sometimes people with chronic infections may not even know they're infected because they won't have any symptoms. An case of chronic infection is Hepatitis C. Most people with Hepatitis C don't even know they're infected and recovery is rare. Nigh 85% of infected people become chronically infected with serious signs of liver damage not appearing until at least 20 years later on the infection begins.
The symptoms of a latent infection may or may not come back after the initial symptoms take disappeared. Latent infections are unique because they may "wake-upward" and reactivate anytime afterwards the infection appears to have gone away. They tin can go from being inactive to agile and back again for months or years. In an agile country, the germs can spread and infect other people, but once in an inactive state, the germs remain subconscious inside the body without effect. An example of a latent infection is the chickenpox. After the initial infection, the virus will hide in the body and may appear once more years later to cause the painful affliction usually known every bit Shingles.
How Can I Be Safe From these Germs?
To avoid getting or spreading germs you must get rid of them and at that place are different ways you can stop them in their tracks before they make y'all sick. Allow'southward acquire how!
Washing your hands is i of the easiest and near effective things you lot tin practice to get rid of germs. To make sure that all the germs on your easily are gone, you lot should briskly wash your easily with soap and water for at to the lowest degree 15 seconds – the aforementioned amount of time information technology takes to sing the alphabet or Happy Altogether. Yous should always wash your hands earlier making or eating nutrient and afterwards coughing, sneezing, bravado your nose, changing a diaper and using the bathroom.
There are also medicines called vaccines that volition prevent y'all from getting sick. In that location are vaccines to forestall measles, whooping cough, chickenpox and meningitis. At that place are also vaccines for those who travel around the world to areas that may have some diseases that aren't common hither. These vaccines volition prevent infection with yellow fever, polio, typhoid fever, hepatitis A, cholera, rabies and other infections.
Our Work has But Begun…
Information technology was once idea that with the invention of different medications and vaccines that scientific discipline had won the war between humans and illness-causing microbes. Nosotros at present know this isn't the instance considering new microbes and diseases are still being discovered and old microbes that were once thought defeated are re-emerging. Foreign new diseases seem to appear out of nowhere, especially at present that more people are traveling internationally. Environmental changes to a microbe can also make information technology a health threat to humans, creating an fifty-fifty bigger concern now that different issues like global warming seem to exist taking effect. The battle between humans and disease-causing microbes is far from over… in fact; you may say its just first.
Glossary
Astute (infection): severe, brusk-term affliction that has a rapid onset.
Athlete'due south Human foot: a contagious fungal foot infection that causes the feet to itch, blister and crack.
Autoimmune disease: when the allowed organisation attacks our body's own cells, tissues and organs, thinking that they are unwanted invaders.
Cancer: any harmful growth or tumor acquired by irregular and uncontrolled cell division; it may spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or the blood stream.
Chickenpox: a very contagious viral infection that causes a blistery ruddy rash.
Cholera: an acute infectious disease of the pocket-size intestine that causes frequent watery diarrhea, vomiting, muscle cramps and astringent dehydration.
Chronic (infection): illness that lasts for a long time, or that shows a common reappearance.
Chronic Lung Disease: a long-term illness that affects the function of the lungs.
Coronary avenue disease: the build-upwardly of cholesterol in the inside layers of the arteries.
Diabetes: a metabolic affliction characterized by excessive urine discharge and constant thirst. Known as: diabetes mellitus or diabetes insipidus.
Hepatitis A: an infection of the liver caused by a virus that is usually spread by swallowing infected food and water. It is also known equally infectious hepatitis.
Hepatitis C: an infection of the liver acquired by a virus that is usually spread by blood and blood products and sometimes through sexual contact.
Immune System: a system (including the thymus, bone marrow and lymphoid tissue) that protects the body from foreign substances and pathogenic organisms past producing an allowed response.
Latent (infection): in a dormant or hidden phase. Also known as hidden or silent infections.
Lymphoid tissue: makes up the lymphatic system – the spaces and vessels between the body organs and tissues through which lymph circulates and removes bacteria and other unwelcome invaders from the torso.
Malaria: an infectious disease that is passed to humans past female mosquitoes. It affects the scarlet blood cells and has fever, chills and sweating as its symptoms.
Measles: an astute, contagious, communicable diseases caused by a virus. It normally occurs in children and causes red spots on the peel, fever and inflammation of the air passages of the caput and pharynx.
Meningitis: inflammation of the membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord, caused by either a leaner (bacterial meningitis) or a virus (viral meningitis). Its symptoms are fever, vomiting, intense headache and potent cervix.
Multiple sclerosis: an autoimmune disease that affects the fundamental nervous system – the brain, spinal cord and optic nerves. The fatty tissue that surrounds the nerves is lost in many areas leaving scar tissue backside. When the fat tissue called myelin is missing, the nerves cannot do their job of passing signals to and from the brain, resulting in the symptoms that are associated with this illness.
Pneumonia: acute or chronic inflammation of the lungs.
Polio: a viral infection that attacks the nerve cells that activate the muscles, the brainstem (the base of the encephalon that connects with the spinal cord) and the spinal cord.
Rabies: an acute, infectious and often fatal illness that attacks the central nervous system (brain and spinal string) and is passed to humans by the bite of an infected animal.
Shingles: a affliction in adults acquired by the same virus that causes chickenpox in children. It causes an inflammation of the spinal and cranial sensory nerve cells that will result in the appearance of blisters or cysts forth the afflicted nerve path. Information technology usually affects only one side of the body and causes sudden, severe attacks of pain.
Sinusitis: inflammation of a sinus or the sinuses, peculiarly in the nasal surface area.
Strep Throat: a throat infection that causes fever and inflammation of the tonsils.
Thymus: a small glandular organ found behind the superlative of the breastbone. Information technology'due south mostly made up of lymphatic tissue and is the site of T cell (a type of white blood cell) differentiation.
Tuberculosis: an infectious disease that is characterized by the germination of tubercles on the lungs and other tissues of the body. A tubercle is a nodule or swelling, peculiarly a mass of lymphocytes (white blood cells) and epithelioid cells (cells that resemble epithelium) that form the wound of tuberculosis.
Typhoid fever: an astute, infectious disease caused by bacteria that is spread by contaminated food or h2o. Its symptoms include fever, headache, cough, bleeding intestines and rose-coloured spots on the skin.
Urinary Tract Infection: an infection of any organ (kidneys, ureters, urethra) of the urinary tract (tract involved in the germination and excretion of urine).
Vaccine: a mixture made upwards of weak or dead disease-causing microbes that is given to prevent, meliorate or care for an infectious disease.
Whooping cough: a bacterial infection that has symptoms including runny olfactory organ, low-grade fever, inflammation of the centre membrane and a feature coughing that ends in a 'whoop' caused past the forceful inspiration of air.
Yellowish fever: an infectious tropical illness that is passed past mosquitoes. Those infected will have high fever, jaundice (a yellowing of the peel), black vomit, an absence of urination and haemorrhage in the digestive tract.
Was this data helpful? Please chip in $v to help us update and expand our educational programs similar Operation Water Health! Or donate $xx or more and receive an Official Donation Receipt for Income Revenue enhancement Purposes.
Source: https://www.safewater.org/fact-sheets-1/2017/1/23/disease-causing-microorganisms
Posted by: ahrenscastis.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Feature(S) Of The Skin Protect(S) Us Against Microbes Such As Bacteria?"
Post a Comment